练习 Exercises
- 分角色朗读课文 Role-play the dialogs.
- 根据课文内容回答问题 Answer the questions based on the dialogs.
- 小王今天来学校了吗?Xiǎo Wáng jīntiān lái xuéxiào le ma?
- 他看见小王了没有?Tā kànjiàn Xiǎo Wáng le méiyǒu?
- 为什么他今天不想吃羊肉?Wèi shénme tā jīntiān bù xiǎng chī yángròu?
- 为什么昨天他们都没去打篮球?
Wèi shénme zuótiān tāmen dōu méi qù dǎ lánqiú? - 小张为什么去北京?Xiǎo Zhāng wèi shénme qù Běijīng?
- 用本课新学的语言点和词语描述图片
Describe the pictures using the newly-learned language points and words.
Zhèr de yīfu jiànjiàn
这儿的衣服________ (件件)。
Nǚháirmen gègè
女孩儿们______ (个个)。
Yīnwèi tiānqì hěn lěng, suǒyǐ wǒ
因为 天气 很 冷,所以 我______ 。
Yīnwèi suǒyǐ wǒmen zài jiā chī wǎnfàn.
因为 ______,所以 我们 在家 吃 晚饭。
语音 Pronunciation
句子的逻辑重音 Logical Stress in a Sentence 06-5
一个句子中,说话人想要表达比较重要的信息或者内容,往往要说得重一些,这个重读的成分就叫作逻辑重音。逻辑重音又叫强调重音。
In a sentence, the information or content that the speaker focuses on is usually stressed. This is called the logical stress or emphatic stress.
在不同语境中,逻辑重音出现在不同的位置。例如:
The logical stress may appear at different positions in different contexts. For example:
Shéi zài fángjiān xuéxí Hànyǔ ne?
A:谁 在 房间 学习 汉语 呢?
Tā zài fángjiān xuéxí Hànyǔ ne.
B:他在 房间 学习 汉语 呢。
Tā zài nǎr xuéxí Hànyǔ ne?
A:他在哪儿学习 汉语 呢?
Tā zài fángjiān xuéxí Hànyǔ ne.
B:他在 房间 学习 汉语 呢。
同样一句话,逻辑重音的位置不同,语义的重点也会发生变化。例如:
The same sentence may have different semantic focuses when the position of the logical stress differs. For example:
Tā zài fángjiān xuéxí Hànyǔ ne.
A:他在 房间 学习 汉语 呢。
(是他在房间学习汉语,不是别的人。
It is him who is studying Chinese in the room, not other people.)
Tā zài fángjiān xuéxí Hànyǔ ne.
B:他在 房间 学习 汉语 呢。
(他是在房间学习汉语,不是在别的地方。
He is studying Chinese in the room rather than in other places.)
汉字 Characters
认识独体字 Single-Component Characters
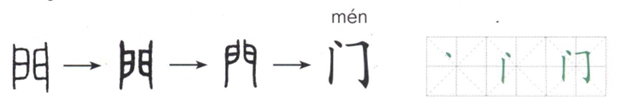
(1)“门”,本义是房屋入口处可开关的两块门板。
“门” originally referred to the two panels of a door at the entrance of a house, which can open and close.
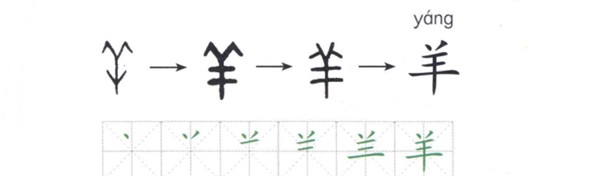
(2)“羊”,字形像正面的羊头,表示“羊”的意思。
The original form of “羊” looks like a sheep’s head facing us. It means “sheep”.
yáng
2 汉字偏旁“犭”和“心” Chinese Radicals: “犭” and “心”
| 偏旁 Radical |
解释 Explanation |
例字 Example Characters |
|---|---|---|
| 犭 | 反犬旁,一般和动物有关系。 The radical “犭” is usually related to animals. |
猫 māo cat 狗 gǒu dog |
| 心 | 心字底,一般和人的思想活动及情感有关系。 The radical “心” is usually related to one’s mental activities and emotions. |
想 xiǎng to think 念 niàn to miss |
运用 1 双人活动 Pair Work
两人一组,选择下列短句,用 “因为……,所以……” 练习说句子。
Work in pairs. Choose appropriate expressions from these given below and use “因为……,所以……” to make sentences.
例如:A: 因为 天气不好,
suǒ yǐ wǒ méi qù shāng diàn.
B: 所以我没去 商店。
- ①工作 太忙 gōng zuò tài máng
- ②不能 去跑步 bù néng qù pǎo bù
- ③汉字太难了 Hàn zì tài nán le
- ④我不喜欢 写汉字 wǒ bù xǐ huan xiě Hàn zì
- ⑤下雨了 xià yǔ le
- ⑥不能 去旅游 bù néng qù lǚ yóu
- ⑦身体 不好 shēn tǐ bù hǎo
- ⑧天天 吃药 tiān tiān chī yào
2 小组活动 Group Work
3~4人一组,用 “怎么” 互相提问并回答,每组请一位同学报告情况。
Work in groups of 3 – 4. Ask and answer questions using “怎么”. Each group chooses a member to make a report.
例如:A: 你 怎么 不吃了?
Nǐ zěnme bù chī le?
B: 我 吃好了。
Wǒ chīhǎo le.
| 问题 Question | 回答 Answer | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 不高兴 bù gāoxìng | 考试没考好。 Kǎoshì méi kǎohǎo. |

评论